
Oct 26, 2025 | Uncategorized
Key points Copper tubes are used in industrial heat exchangers for their excellent thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, strength, and easy fabrication. Copper and copper-nickel alloys ensure efficient, durable, and low-maintenance performance in power plants,...
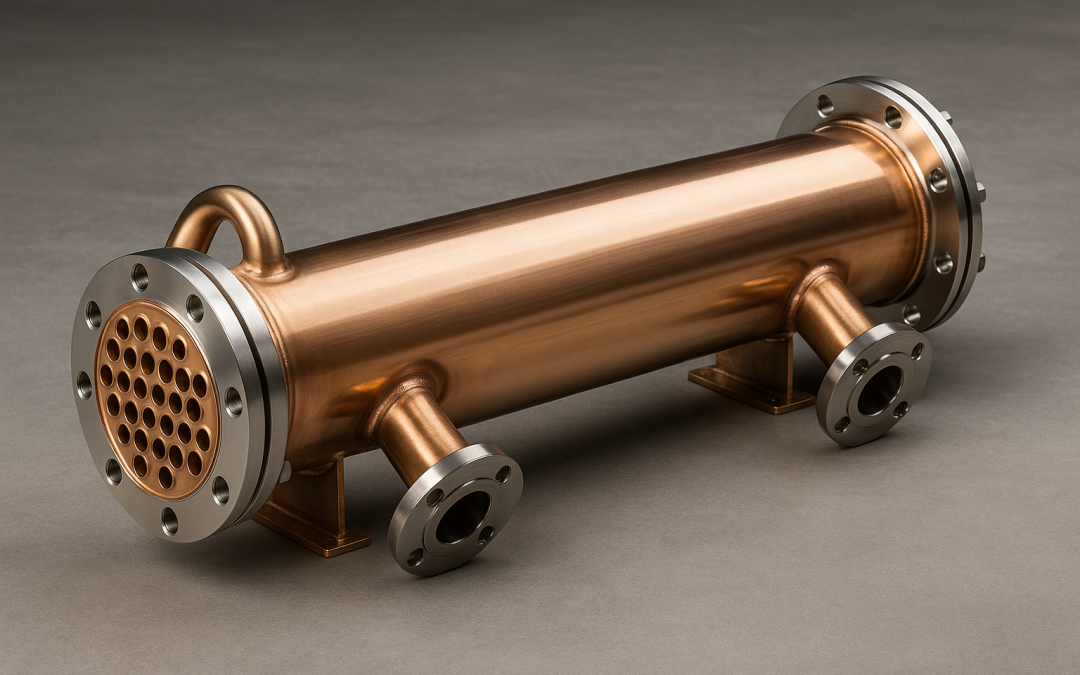

Oct 12, 2025 | Uncategorized
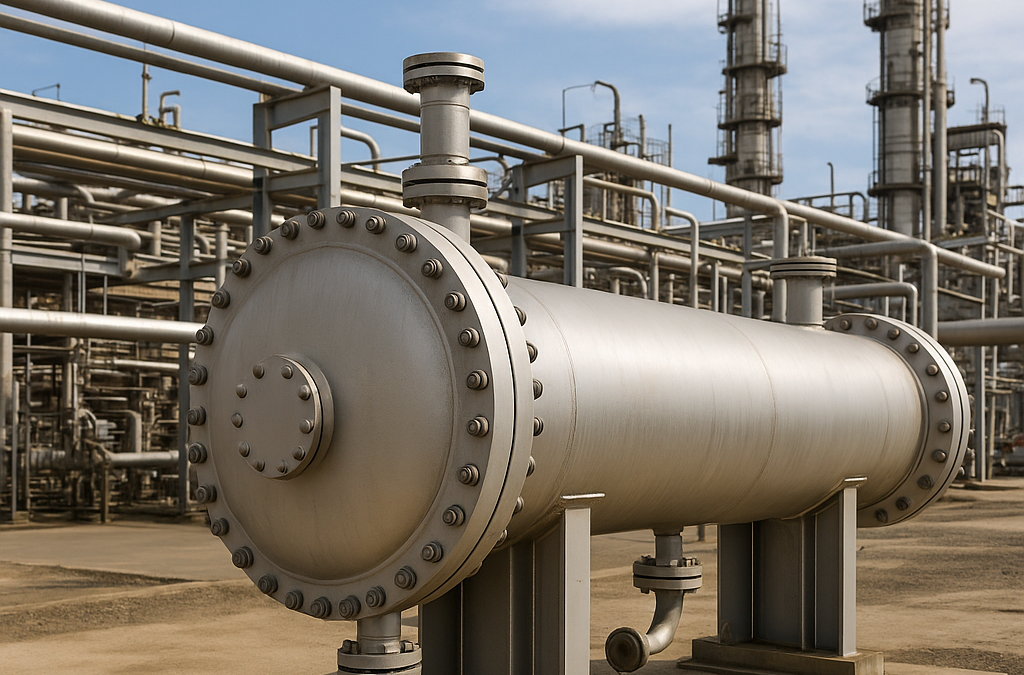
Key points An industrial heat exchanger transfers thermal energy between two fluids without mixing them. It’s a vital component in most process industries, ensuring efficient heating, cooling, condensation, or evaporation. Common designs include plate, shell-and-tube,...

Sep 13, 2025 | Uncategorized
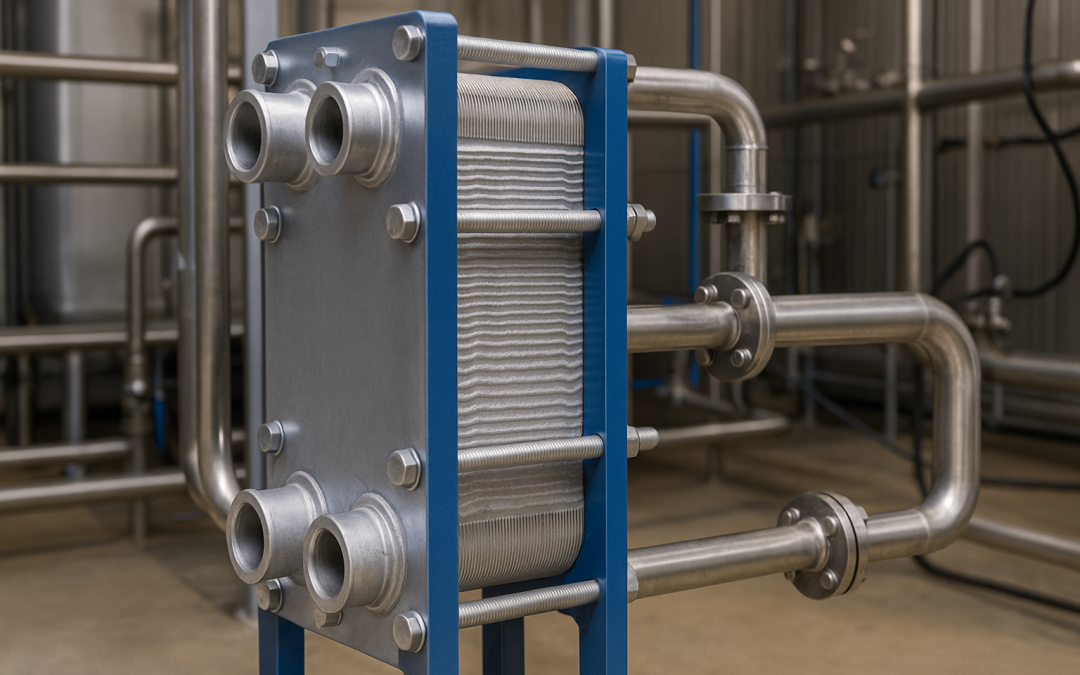
Key points An industrial plate heat exchanger is a device designed to transfer heat between two separate fluids through thin metal plates. It is used in industrial processes to heat or cool fluids, recover thermal energy, improve energy efficiency, and reduce...

Sep 7, 2025 | Uncategorized
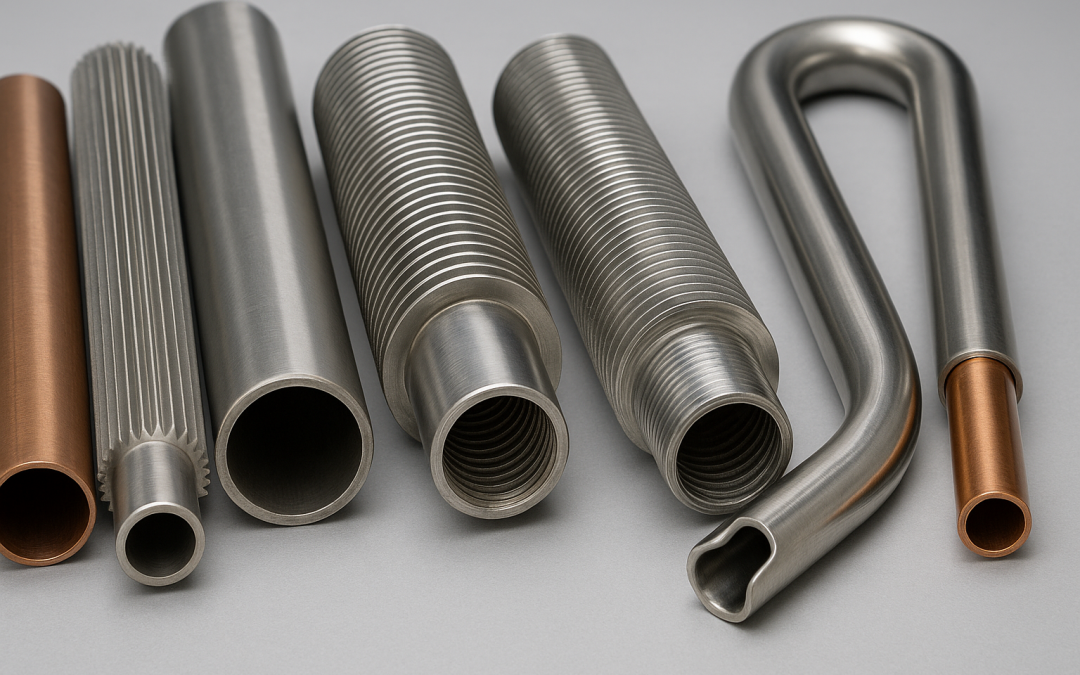
Key points There are several types of heat exchanger tubes, including smooth, finned, rifled, U-tube, and double-pipe designs. Materials vary from stainless steel and copper to titanium and carbon steel. Each type offers unique benefits in terms of heat transfer...
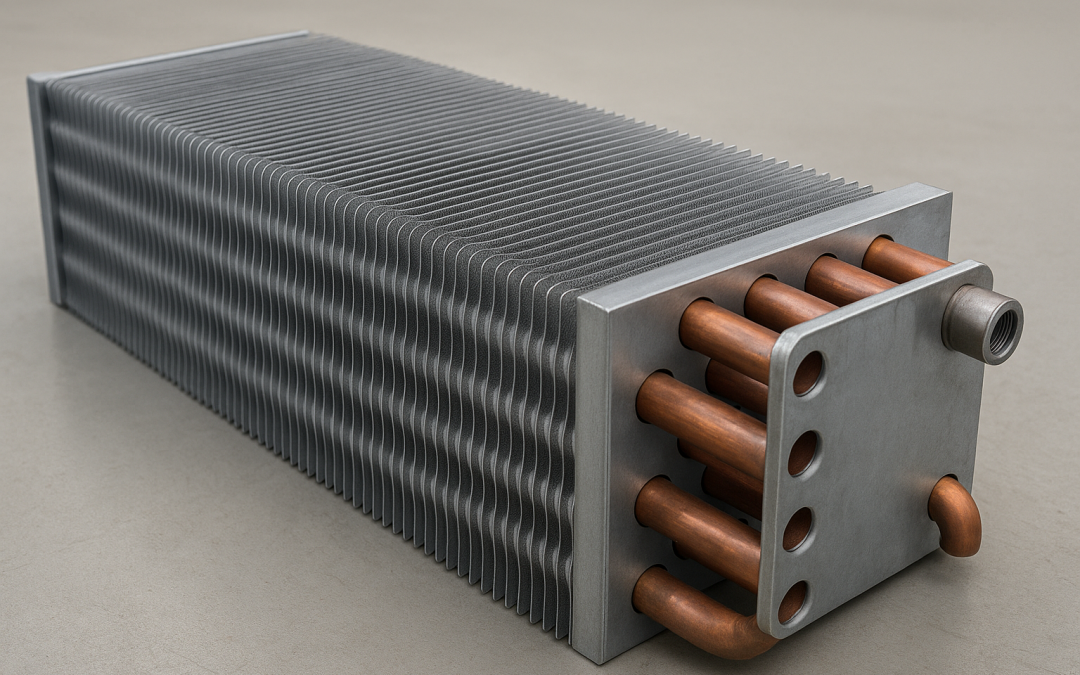
Aug 19, 2025 | Uncategorized
Key points Fin and tube heat exchangers (often called “finned-tube” coils) boost heat transfer by adding fins to round or flat tubes, increasing surface area on the air side. They are common in HVAC coils, power plants, petrochemical coolers, and marine systems. To...

Aug 12, 2025 | Uncategorized
Key points The best tube materials for shell-and-tube heat exchangers depend on fluid chemistry, temperature, velocity, and fouling risk. Cu-Ni 90/10 and 70/30 excel in natural seawater; aluminum brass (C68700) works in cleaner chloride waters; titanium (Grade 2)...






